A new article reporting findings on age-related variation in how people use patient accessible electronic health records has been published in Information Technology and People. The study is collaborative work between HIBA project and Swedish DOME research consortium and is freely available as open access.
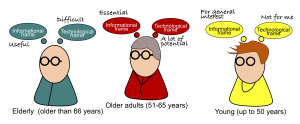
The results show that younger respondents of a survey study conducted in Sweden were more likely to be interested in PAEHR contents for general interest. They did not value online access to the information as high as older ones. Older respondents were instead inclined to use medical records information to understand their health condition, prepare for visits, become involved in their own healthcare and think that technology has a much potential. Moreover, the oldest respondents were more likely to consider the information in the patient accessible electronic health records useful and aimed for them but to experience the technology as inherently difficult to use.
The study shows also how people in different ages think differently about information and technology, and how information technologies like patient accessible electronic health records should be studied separately from information and technology perspectives. People can have different views of technologies and the information they are used to make available. To understand the different views, the study suggests to look not only to people’s technological but also to their informational frames of reference.
Citation
Huvila, I., Cajander, Å., Moll, J., Enwald, H., Eriksson-Backa, K. and Rexhepi, H.(2021), “Technological and informational frames: explaining age-related variation in the use of patient accessible electronic health records as technology and information”, Information Technology & People, Vol. ahead-of-print No. ahead-of-print. https://doi.org/10.1108/ITP-08-2020-0566
Abstract
Purpose
Data from a national patient survey (N = 1,155) of the Swedish PAEHR “Journalen” users were analysed, and an extended version of the theory of technological frames was developed to explain the variation in the technological and informational framing of information technologies found in the data.
Design/methodology/approach
Patient Accessible Electronic Health Records (PAEHRs) are implemented globally to address challenges with an ageing population. However, firstly, little is known about age-related variation in PAEHR use, and secondly, user perceptions of the PAEHR technology and the health record information and how the technology and information–related perceptions are linked to each other. The purpose of this study is to investigate these two under-studied aspects of PAEHRs and propose a framework based on the theory of technological frames to support studying the second aspect, i.e. the interplay of information and technology–related perceptions.
Findings
The results suggest that younger respondents were more likely to be interested in PAEHR contents for general interest. However, they did not value online access to the information as high as older ones. Older respondents were instead inclined to use medical records information to understand their health condition, prepare for visits, become involved in their own healthcare and think that technology has a much potential. Moreover, the oldest respondents were more likely to consider the information in PAEHRs useful and aimed for them but to experience the technology as inherently difficult to use.
Research limitations/implications
The sample excludes non-users and is not a representative sample of the population of Sweden. However, although the data contain an unknown bias, there are no specific reasons to believe that it would differently affect the survey’s age groups.
Practical implications
Age should be taken into account as a key factor that influences perceptions of the usefulness of PAEHRs. It is also crucial to consider separately patients’ views of PAEHRs as a technology and of the information contained in the EHR when developing and evaluating existing and future systems and information provision for patients.
Social implications
This study contributes to bridging the gap between information behaviour and systems design research by showing how the theory of technological frames complemented with parallel informational frames to provide a potentially powerful framework for elucidating distinct conceptualisations of (information) technologies and the information they mediate. The empirical findings show how information and information technology needs relating to PAEHRs vary according to age. In contrast to the assumptions in much of the earlier work, they need to be addressed separately.
Originality/value
Few earlier studies focus on (1) age-related variation in PAEHR use and (2) user perceptions of the PAEHR technology and the health record information and how the technology and information–related perceptions are linked to each other.
Keywords
- Information seeking behaviour
- End users
- Technology
- Theoretical concepts